Diagnosis
 One Person Dies From Oral Cancer Nearly Every Hour Of Every Day. The most important step in reducing the death rate from oral cancer is early discovery. The oral cancer death rate is high due to late discovery. Oral cancer detection is the primary responsibility of the dental community. The introduction of VELscope powered by Sapphire at Ferrari Dental clinics, allows a Painless, Fast, Non- Invasive, Positive identification of oral cancers at the Earliest Stages, and results in the best prognosis for cure and long-term survivability. We would recommend performing an oral cancer self-examination monthly and remember that your mouth is one of your body's most important warning systems. Do not ignore suspicious lumps or sores, please contact us so we may help you.
One Person Dies From Oral Cancer Nearly Every Hour Of Every Day. The most important step in reducing the death rate from oral cancer is early discovery. The oral cancer death rate is high due to late discovery. Oral cancer detection is the primary responsibility of the dental community. The introduction of VELscope powered by Sapphire at Ferrari Dental clinics, allows a Painless, Fast, Non- Invasive, Positive identification of oral cancers at the Earliest Stages, and results in the best prognosis for cure and long-term survivability. We would recommend performing an oral cancer self-examination monthly and remember that your mouth is one of your body's most important warning systems. Do not ignore suspicious lumps or sores, please contact us so we may help you.
Why should I get screened with VELscope powered by Sapphire?
One of the real dangers of this cancer is that in its early stages, it can go unnoticed. It can be painless, and little in the way of physical changes may be obvious.

The advantages of VELscope oral cancer screening include:
- Allows early detection that can save your life.
- Detects lesions that aren't even visible.
- Procedure is painless and takes only minutes.
- Gives the dentist a clear, up- close look at the condition of your mouth.
- Digital camera allows your dentist to document findings for records and to ensure accurate treatment.
How does it work?
The patented VELscope technology platform was developed in collaboration with the British Columbia Cancer Agency and MD Anderson Cancer Center, with funding provided in part by the NIH.
It is based on the direct visualization of tissue fluorescence and the changes in fluorescence that occurs when abnormalities are present.
The VELscope Handpiece emits a safe blue light into the oral cavity, which excites the tissue from the surface of the epithelium through to the basement membrane (where premalignant changes typically start) and into the stroma beneath, causing it to fluoresce. The clinician is then able to immediately view the different fluorescence responses to help differentiate between normal and abnormal tissue.
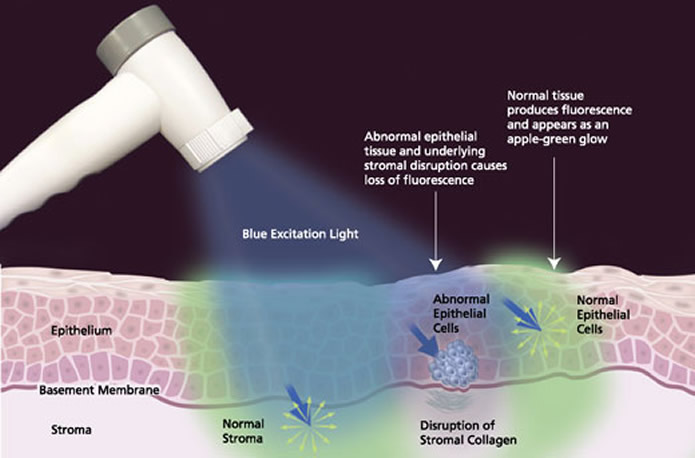
Typically, healthy tissue appears as a bright apple-green glow while suspicious regions are identified by a loss of fluorescence, which thus appear dark.
Tongue cancer: velscope screening shows the lesions that may have escaped the traditional oral cancer detection
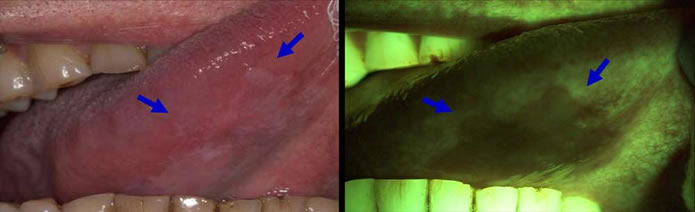
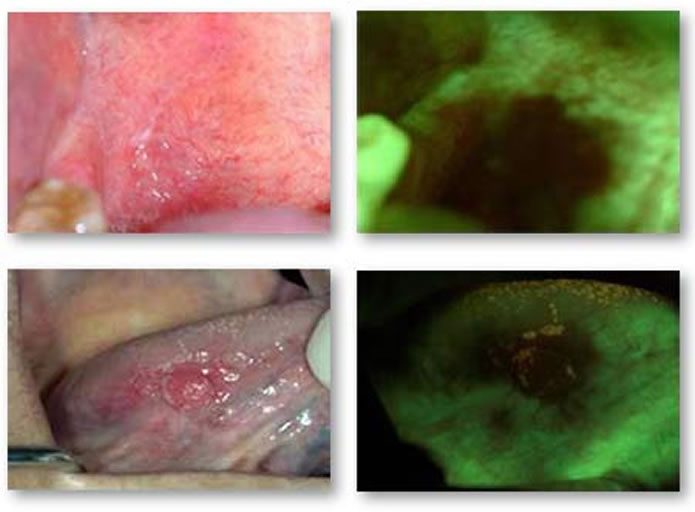
Velscope screening for oral cancer detection
Oral cancer risk factors:
 More common in men than women.
More common in men than women.- Most common in African Americans.
- Greater risk after age 35.
- Tobacco use
- Frequent alcohol consumption.
- Prolonged exposure to sunlight (lip cancer)
- A diet low in fruits and vegetables.
- The sexually transmitted infection HPV that has caused an increase of cases in young, non- smoking individuals, a group that, until recently, had a low rate of oral cancer incidence.
However, approximately 25% of oral cancer cases have no known risk factors.
Signs & Symptoms:
The inside of the mouth is normally lined with a special type of skin (mucosa) that is smooth and coral pink in color. Any alteration in this appearance could be a warning sign for a pathological process. Some of the most common are mucosal lesions, oral precancer, tongue lesions, lip lesions, salivary diseases, tooth defects, anomalies, odontogenic cyst, leukoplakia (whitish patches in the mouth), candidiasis, lichen planus, recurrent canker sores, bone disease, erythroplakia (reddish patches in the mouth), aphthous ulcerations, geographic tongue, and tobacco keratosis. The most serious of these is oral cancer. - Pain is not always necessary to define pathology and, curiously, is not often associated with oral cancer.
It is important to have any sore or discolored area of your mouth, which does not heal within 14 days, looked at by a professional.
The following can be signs at the beginning of a pathologic process or cancerous growth:
- A white or red patch of tissue in the mouth,
- A small indurate ulcer, which looks like a common canker sore.
- A lump or mass, which can be felt inside the mouth or neck,
- Pain or difficulty in swallowing, speaking, or chewing,
- Any wart like masses,
- Hoarseness, which lasts for a long time,
- Any numbness in the oral/facial region.
Certainly, it is common knowledge that two of the most prevalent lesions that mimic oral cancer, are the herpes simplex ulceration, and aphthous ulcerations, each resolving of their own accord in approximately 10-14 days.
Conventional oral cancer examination procedure:
This procedure involves systematic visual examination of all the soft tissues of the mouth, including manual extension of the tongue to examine its base, a bi-manual palpation of the floor of the mouth, and a digital examination of the borders of the tongue, and the lymph nodes surrounding the oral cavity and in the neck. New diagnostic aids, including lights, dyes, and other techniques are making the discovery process more effective. Once suspect tissues have been detected, the only way a definitive diagnosis of oral cancer may be made is through biopsy.