Gum Graft
The Best Gum Graft Surgeons in Beirut Lebanon
Grafting is a procedure used to replace / restore missing bone or gum tissue. A gingival graft (also called gum graft or periodontal plastic surgery) is a generic name for any of a number of surgical periodontal procedures whose combined aim is to cover an area of exposed tooth root surface with grafted oral tissue. The covering of exposed root surfaces accomplishes a number of objectives: * Prevention of further root exposure, * Decreased or eliminated sensitivity, * Decreased susceptibility to root caries, * Improved cosmetic.
Ferrari Dental Clinics Technique:
Perhaps you wish to enhance your smile by covering one or more of these roots that make your teeth appear too long. Or, maybe you're not bothered by the appearance of these areas, but you cringe because the exposed roots are sensitive to hot or cold foods and liquids.
Waterlase technology allows to perform gum grafting procedures in minutes with virtually no bleeding at the operated site. In most cases, it is not necessary to take painful gum grafts from other parts of the mouth, like the palate. Precise Waterlase energy sterilizes the area, dramatically reducing postoperative discomfort and promoting faster healing.
Connective tissue graft:
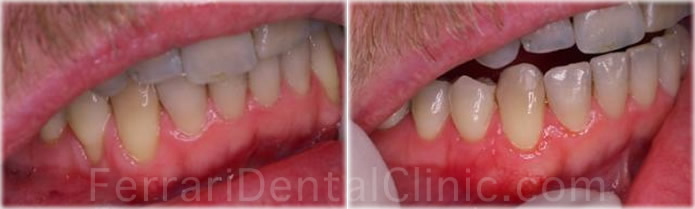
Types of gum tissue:
There are two types of gum tissue in the mouth, one of which surrounds the necks of the teeth and is thick and protective in nature (keratinized gingiva).
The other of which lines our cheeks and floor of the mouth whose purpose is to be elastic and mobile in nature (mucosa).
Why is a gum graft needed?
- Gum recession:
When there is only minor recession, some healthy gingiva often remains and protects the tooth, so that no treatment other than modifying home care practices is necessary.
However, when recession reaches the mucosa, the first line of defense against bacterial penetration and trauma is lost.
In addition, gum recession often results in root sensitivity to hot and cold foods as well as an unsightly appearance to the gum and tooth. Gum recession, when significant, can predispose to worsening recession and expose the root surface, which is softer than enamel, leading to root caries and root gouging.
Free Gingival Graft:
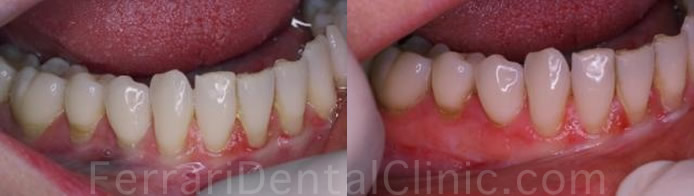
What causes recession?
Aggressive brushing - potentially? Some people believe that aggressive brushing with a hard bristled brush may be a co-factor in recession or erosion of the neck of the tooth.
Excessive biting forces - clenching and/or grinding? This can result in bending / flexing of teeth, which will often result in fracture of a small portion of tooth structure at the gum line (abfractions) and consequently bone and gum recession.
Maloccluded and misaligned teeth? Teeth that positioned outside the normal arch form of the jaw are subject to having abnormal forces placed on them causing recession.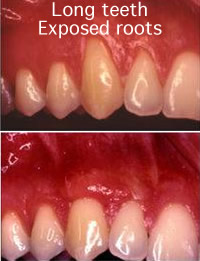 When treating recession by gum grafting, the causative factor must also be addressed in order for the grafting procedure to be successful.
When treating recession by gum grafting, the causative factor must also be addressed in order for the grafting procedure to be successful.
- Cosmetic Gum Grafts:
Esthetic gum grafting can be used to "plump up" the gum tissue in an area that is deficient and would result an unaesthetic cosmetic makeover. Remember the teeth and gums should exhibit symmetry, yet sometimes one side is deficient, therefore, gum grafting may be essential to achieve symmetry prior to a cosmetic make-over.
What are the conventional techniques of Gum Grafts?
- A free gingival graft is a dental procedure where a layer of tissue is removed from the palate of the patient's mouth or gently moved over from adjacent areas and then relocated to the site of gum recession. It is stitched into place and will serve to protect the exposed root as living tissue by providing a stable band of attached gingiva around the tooth. The donor site will heal without damage. This procedure is often used to increase the thickness of very thin gum tissue. The gingival graft procedure is highly predictable and results in a stable, healthy band of attached tissue around the tooth.
- A subepithelial connective tissue graft takes tissue from under healthy gum tissue in the palate, which may be placed at the area of gum recession. This procedure has the advantage of excellent predictability of root coverage, as well as decreased pain at the palatal donor site compared to the free gingival graft. The subepithelial connective tissue graft is used to not only restore missing thick keratinized gum tissue, but also used to cover exposed roots of the teeth.
- An acellular dermal matrix (such as Alloderm) graft uses donated medically-processed human skin tissue as a source for the graft. The advantage of this procedure is no need for a palatal donor site, however some periodontists believe it may be less successful, while others believe it is equally successful as a subepithlial connective tissue graft.
- A lateral pedicle graft, or pedicle graft, takes tissue from the area immediately adjacent to the damaged gingiva. This is not always an option, as the constraint that there must be sufficient tissue immediately lateral to the area of interest is an onerous one. When this procedure is performed, the transplant tissue is cut away and rotated over the damaged area. This can place the donor area at risk of recession as well.
- Coronally and apically positioned flaps, although technically not grafting procedures, are other forms of a pedicle grafts in that gingival tissue is freed up and moved either coronally or apically. This requires adequate thickness and width of gingival tissue at the base of the recession defect.